In this post, we will explore the advantages and risks of crypto ETFs in a portfolio, but first, our disclosure:
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, meaning we earn a commission on purchases made through those links at no extra cost to you. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Disclaimer: The content on this site is for informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, legal, tax, or any other professional advice and should not be used as a substitute for professional advice. For more details, read our full Disclaimer.
How Much Crypto Should Be In Your Portfolio?
Cryptocurrencies are known for their high risk and extreme volatility. Their price swings can cause whiplash. Due to these factors, many financial experts recommend limiting cryptocurrency to less than 5% of one’s total investment portfolio. In other words, for every $100 invested, no more than $5 should be in cryptocurrency.
For beginner crypto investors, they suggest starting at 1% to 2%. So, for every $100 invested, no more than $1 to $2 should go to crypto.
To clarify, these experts do not recommend that everyone have crypto in their portfolio. But if someone does, they recommend keeping it on the lower end due to its risk.
No matter which advice you choose to follow, always remember that diversification and education are the keys to investing.
Risk, Diversification, and Research
Putting all your money into a single investment, like Bitcoin, is risky. The chart below shows Bitcoin’s yearly return from 2014 to 2023. Look at those price swings. Bitcoin is either up 50% or more in a year or down 50% or more. Have you ever seen an investment up 1,163% one year and down 72% the next? That is why it is so crucial to diversify.
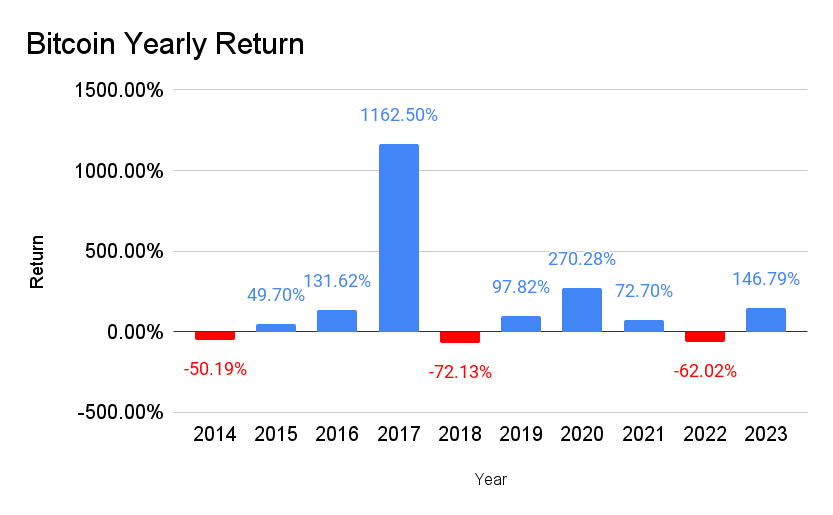
Diversification helps lower risk by spreading investments across and within different asset classes. But it does not eliminate risk—nothing does. That is why it is critical to do your due diligence and research before investing.
If you are interested in crypto, take the time to understand the available investment options. As you will soon see, there are many options in crypto ETFs in addition to the thousands of cryptocurrencies that exist.
Researching an investment takes time but is never a waste of time. Read books and articles from reputable authors, listen to credible podcasts, and track the investment for a while. Remember, it is your money and your responsibility.
My first foray into crypto was a disaster. I wish I had spent more time learning about crypto. I thought I was playing safe by investing in Coinbase stock rather than buying Bitcoin. But then the worst inflation in 40 years hit, and I lost 80% of my Coinbase investment. Since then, I’ve avoided anything related to cryptocurrencies—that is, until now.
Since then, I have spent time educating myself on cryptocurrencies. I strongly recommend reading two books: “The Bitcoin Standard” and “The Fiat Standard.” by Saifedean Ammous.
So, let’s get to it and learn about crypto ETFs, starting with the basics.
What Are Crypto ETFs?
A cryptocurrency exchange-traded fund (crypto ETF) provides a more straightforward way for individuals to invest in cryptocurrencies, eliminating the complexities of buying crypto directly and the concerns of storing it.
Crypto ETFs trade on traditional exchanges like regular stocks, providing a simple and regulated way to invest in the crypto market. However, they are risky and may not always reflect the prices of the cryptocurrencies they represent.
There are two primary types: spot crypto ETFs, which hold actual cryptocurrencies, and futures-based crypto ETFs, which invest in futures contracts tied to crypto prices. In addition to these two, there are additional crypto ETFs, like inverse (Short-selling) ETFs and leveraged ETFs. But these take the risk of cryptocurrency to the stratosphere.
What’s The Difference Between Crypto ETFs?
The big difference is that spot crypto ETFs hold actual cryptocurrency, while the other crypto ETFs do not.
Let’s look at each in more detail, starting with the new spot crypto ETFs.
Spot Crypto ETFs
Example: Fidelity Wise Origin Bitcoin (FBTC)
When people say crypto ETFs, chances are they are referring to spot crypto ETFs. They are all the rage today and the main reason I am considering investing in crypto.
Crypto spot ETFs closely track cryptocurrency price movements by holding the actual cryptocurrency they are tracking. The spot crypto ETF then issues shares corresponding to the number of the specific cryptocurrency in the fund. In doing so, a spot crypto ETF’s price correlates to the current market price of the cryptocurrency it holds.
For instance, a Bitcoin spot ETF would be composed of 100% Bitcoin and issue shares based on the number of Bitcoins it holds. In turn, the value of the Bitcoin spot ETF would rise or fall based on the price of Bitcoin.
The Birth Of Spot Crypto ETFs
In 2024, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approved spot crypto exchange-traded funds (ETFs) for Bitcoin and Ethereum. Before the introduction of spot crypto ETFs, the primary way to invest in crypto was to purchase it directly through exchanges, futures contracts, or crypto ETFs that did not directly hold crypto.
What Cryptocurrencies Are Approved For Spot Crypto ETFs?
As of this writing, the SEC has approved spot crypto ETFs for Bitcoin and Ethereum (Ether). Given that Bitcoin and Ethereum are the two largest cryptocurrencies, it is unsurprising that the SEC has approved them as the first crypto ETFs. However, given thousands of cryptocurrencies, the SEC may approve other crypto ETFs in the years ahead.
What is the Difference Between Bitcoin and Ethereum?
Many people outside crypto’s orbit might think all cryptocurrencies serve the same purpose, but that is not true. While Bitcoin and Ethereum share the goal of decentralization using a public ledger called blockchain, that is where their similarities end and their differences begin.
Purpose of Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a digital currency designed to enable people to transact with each other without the need for a central bank or government. It uses a public blockchain to verify and record each transaction. As transactions are verified, new bitcoins are created through a process known as “mining, ” which involves solving complex math problems.
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency created, and there will ever be only 21 million Bitcoins. Due to its scarcity and function as a store of value, Bitcoin is often called “digital gold.”
Purpose of Ethereum
Ethereum is a decentralized software platform that acts like a global computer. It allows people to build and run decentralized applications and smart contracts on its blockchain. These smart contracts are programs that automatically execute actions when certain conditions are met, like transferring money or verifying information.
Ethereum’s cryptocurrency, Ether, is used for transactions on the Ethereum network. Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum does not cap the supply of Ether.
So, while Bitcoin is digital gold, Ethereum is more like digital silver. It offers a flexible platform for creating and running decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts.
One thing to note is that people often use Ethereum and Ether interchangeably when discussing crypto, much like I have done throughout this post.
Crypto Futures ETFs
Example: Proshares Bitcoin Strategy ETF (BITO)
Cryptocurrency futures ETFs do not hold the cryptocurrency they track. Instead, they buy and sell futures contracts intending to replicate the spot price of a cryptocurrency. Their performance is based on the value of futures contracts, not the actual cryptocurrency. As a result, the value of these ETFs may not match the spot price of the cryptocurrency they mirror.
If you are unfamiliar with futures contracts, they are agreements between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a future date. When someone engages in futures contracts, they speculate on the future price of an asset or commodity.
Let’s look at an oversimplified example of futures contracts using Bitcoin.
Example Of Bitcoin Futures Contract
Let’s say Bitcoin is currently at $50,000, and you predict its price will increase over the next six months. You purchase a Bitcoin futures contract, representing one Bitcoin at $50,000. When the contract expires in six months, there are two possible outcomes: Bitcoin’s price increased or decreased.
Let’s assume Bitcoin’s price rises to $65,000. That’s fantastic news! You just made a $15,000 profit. Essentially, you bought a $65,000 Bitcoin for $50,000.
But what happens if the price of Bitcoin falls to $35,000 by the end of the contract?
In that case, you would incur a loss of $15,000. In other words, you would purchase a $35,000 Bitcoin for $50,000.
The above is a simple example. Bitcoin is not a physical object, and other factors, such as leverage, amplify the risk of futures contracts. Speaking of leverage, let’s move on to our next type of ETF.
Leveraged Crypto ETFs
Example: Volatility Shares 2X Bitcoin Strategy ETF (BITX)
A leveraged crypto ETF uses debt and derivatives, like futures contracts and swaps, to increase returns. Most leveraged crypto ETFs aim for two times (2X) or three times (3X) the return of Bitcoin for a single day. Notice that I said a single day! Leveraged Crypto ETFs are designed for short-term trading, like day trading, and are not for long-term investing. In short, an investor using leveraged crypto ETFs is attempting to time the market.
To say that leveraged crypto ETFs are risky is a colossal understatement. They combine crypto, speculation, leverage, derivatives, and day trading all in one fund! Can there be anything riskier?
Remember, leveraged crypto ETFs aim to amplify your returns by 2X or 3X, but that works in both directions, up or down. So, there is a chance an investor can lose a lot of money in a leveraged crypto ETF. Therefore, leveraged crypto ETFs are only for investors with a high-risk tolerance, both mentally and monetarily.
Inverse Crypto ETFs
Example: ProShares Short Bitcoin ETF (BITI)
Inverse crypto ETFs aim to protect against falling cryptocurrency prices by betting prices will go down. They aim to deliver the inverse return of the crypto index they are tracking.
It seems simple enough, but it’s not.
Understanding the inner workings of inverse crypto ETFs can be challenging. On the surface, their goal is straightforward: to achieve the opposite performance of the crypto index they track. However, they use some of the riskiest trading strategies ever created to accomplish this goal.
Inverse crypto ETFs use short-selling of futures contracts and other financial products to deliver the inverse return of the crypto index they track. As such, they track the daily movement of crypto prices. Due to this, inverse crypto ETFs are for short-term investors who can handle very high levels of risk.
It’s like parachuting from an airplane into a pool of sharks with a bloody nose. Oh yeah! You need to be able to pay for the experience, too, and it’s not cheap.
Let’s look at an example of why inverse crypto ETFs are risky.
Example Using Inverse Crypto ETFs
You are having a cookout and chatting with your friends. One of your friends is an experienced Bitcoin trader who gives you a hot tip: Bitcoin will drop tomorrow. Convinced of your friend’s genius, you rush to your computer, buy $10,000 of a Bitcoin inverse ETF, and wait for tomorrow.
Great news! Bitcoin dropped 2%, just as your friend said it would, and your inverse ETF rose 2%. You just made $200 in one day. If you can earn 2% or $200 in one day, imagine what you can earn in one year! So, you sit back and wait for the opportunity.
Example of Inverse Crypto ETFs Going Bad
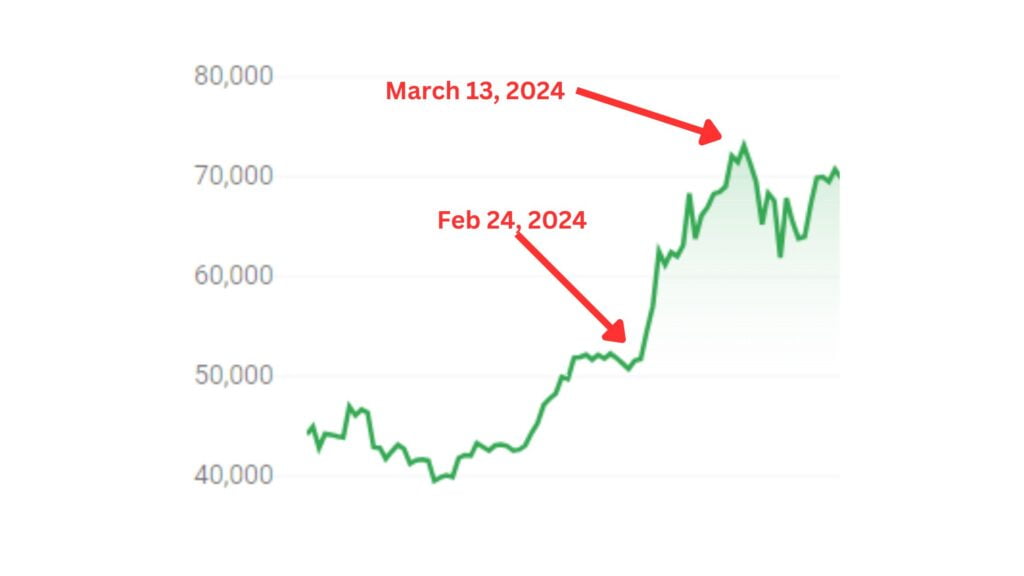
It’s February 23, 2024, and Bitcoin has had a nice run over the last few weeks, rising from $43,000 to $51,000, a 19% increase. You consult with your friend, who consults their fancy charts and tells you Bitcoin will drop big in the next two days. After hearing this prediction, you buy another $10,000 of a Bitcoin inverse ETF.
The next morning, you wake up excited and run to your computer to check the Bitcoin price. Your excitement turns to disappointment. Instead of dropping, Bitcoin’s price rose to $52,000. You tell yourself it has to drop soon; it can’t keep going up.
The next morning rolls around, and Bitcoin is still at $52,000. You breathe a sigh of relief, convinced more than ever that the big drop is about to happen, but it doesn’t. The next day, Bitcoin rises to $54,000, then $57,000, and by Wednesday, February 28, Bitcoin’s price is at $62,500.
You are looking at a 23% loss, as you purchased the inverse ETF when Bitcoin was $51,000. The idea of a 23% loss is too much to bear. Instead of selling, you hold, hoping to get back at least half the losses. That is when things go from bad to worse.
By March 4, 2024, Bitcoin hits $68,000 and keeps climbing, reaching a peak of $73,000 on March 13, 2024. Unable to bear further losses, you sell your position in the inverse crypto ETF. In the span of three weeks, you ended up losing almost half of your investment.
You might think I made up the price movements of Bitcoin to prove a point, but I didn’t. The dates and corresponding Bitcoin prices in the above example are real, as is the risk.
Crypto Industry ETFs
Example: Fidelity Crypto Industry Digital Payments ETF (FDIG)
Crypto industry ETFs focus on companies developing exchanges and blockchain technology. Unlike other crypto ETFs, they do not invest directly in cryptocurrencies or use risky trading strategies involving futures contracts or derivatives.
For instance, as of this writing, the Fidelity Crypto Industry Digital Payments ETF (FDIG) holds 47 companies, including Coinbase, Marathon Digital Holdings, and Cleanspark.
Crypto industry ETFs provide exposure to the crypto industry without the risk of investing directly in cryptocurrency. However, make no mistake: crypto industry ETFs are highly volatile and risky. Companies tied to the crypto industry tend to see their fortunes rise and fall with the price of Bitcoin. I know the dangers firsthand.
In 2021, when Bitcoin was at $60,000, I invested in Coinbase right after its IPO to gain exposure to the crypto industry. I thought I could minimize risk by indirectly investing in crypto instead of buying Bitcoin outright. I was confident in my plan, as Coinbase is the largest crypto exchange in the United States and was turning a profit. Things did not go according to plan.
Bitcoin’s price dropped over the next year, and Coinbase’s profit and share price followed. By the time I sold off my Coinbase position a year later, I had lost over 80%!
To be fair to Coinbase, I made three major boneheaded, superduper, risky investing decisions. I invested in a single stock right after its IPO in a notoriously risky industry. That is the trifecta of a high-risk investment decision!
Pros Crypto ETFs
Easy and Accessible
Investing directly in cryptocurrency can be complicated. You must sign up for an exchange like Coinbase and keep track of public and private keys. You must also be familiar with cryptocurrency wallets and hot and cold storage. This complexity can be a barrier for people who want exposure to crypto but do not intend to use it for transactions.
Cryptocurrency ETFs provide a simpler alternative to directly owning cryptocurrencies. They offer investors an easy way to participate in cryptocurrency through traditional exchanges. Investors can buy and sell them like any other ETF. This ease of use makes cryptocurrency accessible to both beginners and traditional investors.
Regulatory Oversight
Depending on the type of crypto ETF, it can be regulated by either the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) or the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This regulatory oversight helps mitigate some risks of investing in cryptocurrencies by ensuring that the crypto ETF adheres to specific regulatory standards.
Security
Crypto wallets and exchanges can be hacked, and security keys can be stolen. This is not the case with ETFs. When you invest in a crypto ETF, you don’t need to manage wallets or keys because you don’t directly own cryptocurrency. Instead, you own shares of an ETF that may hold cryptocurrencies or crypto derivatives.
Protects Against User Error
People have lost access to their bitcoins by misplacing or destroying the security keys. Some crypto investors store their security keys on a hard drive or scribble them down on paper, but if the hard drive crashes or the paper ends up in the trash, the bitcoins are gone. Almost 4 million bitcoins, or 20% of the total, might be gone forever. It’s like losing the keys to your house and never being able to get inside again.
Owning crypto ETFs prevents user error. You don’t need to worry about storing and securing security keys. The worst thing that can happen is you forget your password to your online brokerage account and have to do a password reset. On the other hand, there are no “password resets” with crypto security keys.
Cons of Crypto ETFs
No Ownership
Investing in a crypto ETF allows someone to gain exposure to crypto without the difficulties of owning and safeguarding it. Unless you invest in a spot crypto ETF, the ETF itself does not directly own crypto. As a result, you cannot use a crypto ETF for transactions.
Volatility and Risk
Whether you own crypto outright or a crypto ETF, you cannot avoid the volatility and risk of cryptocurrencies. While crypto ETFs are regulated, cryptocurrency itself is not. The cryptocurrency markets involve speculation and unregulated trading, leading to wild price fluctuations. Investing in a crypto ETF will not protect you from these fluctuations, so invest at your own risk.
Fees
In most cases, you only need to make a one-time payment when you buy crypto through an exchange. However, when you buy a crypto ETF, you need to pay any trading fees to buy or sell the ETF along with the fund’s expense ratio. The expense ratios for crypto ETFs can be high, exceeding 1%, especially for leveraged, inverse, or futures contracts crypto ETFs.
Spot crypto ETFs tend to have lower expense ratios as they do not require active management or complex trading strategies. Their expense ratios can be 0.25% or lower, making them cheaper than other crypto ETFs..
Trading During Normal Business Hours
Many crypto exchanges allow trading 24 hours a day, seven days a week, while crypto ETFs trade during regular market hours.
Suppose you own a spot Bitcoin ETF. On a Saturday afternoon, you check Bitcoin’s price and see that it is in freefall. There is nothing you can do over the weekend. You must wait until Monday morning when the markets are open to make a trade.
The limits on trading hours for crypto ETFs might be a negative for some traders but a positive for others. It creates a cooling-off period before making a rash decision.
Conclusion: Crypto ETFs
Crypto ETFs come in all shapes and sizes and might be a good addition to a diversified investment portfolio. However, before you run out and buy into one, remember crypto is one of the riskiest and most volatile investments someone can make. For this reason, financial experts often recommend investors limit crypto to less than 5% of their total portfolio.
To put their risk in perspective, Fidelity will not let you invest in their spot Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs unless you sign a “Designated Investments Agreement” attesting to their risk and acknowledging you are an experienced investor. I have over twenty years of experience investing and have never had to sign such an agreement. That should tell you how risky crypto ETFs are.
The key is to do your homework before investing in crypto ETFs or any other investment. After researching, you may discover that crypto ETFs are not for you as they are among the riskiest investments. However, if you determine that they are the right choice for you, there are options available to choose from.
When investing in cryptocurrency ETFs, the main challenge lies in finding ones that suit your needs. There are various types of crypto ETFs, but spot crypto ETFs are the only ones that directly hold the cryptocurrency they track. As a result, they are the closest option to owning actual crypto, like Bitcoin.
The bottom line is that it’s your responsibility to do your homework. Whether Crypto ETFs are right for you is a decision only you can make, So choose wisely!













